Learn more about our mobile apps
Smart Devices, Better Care
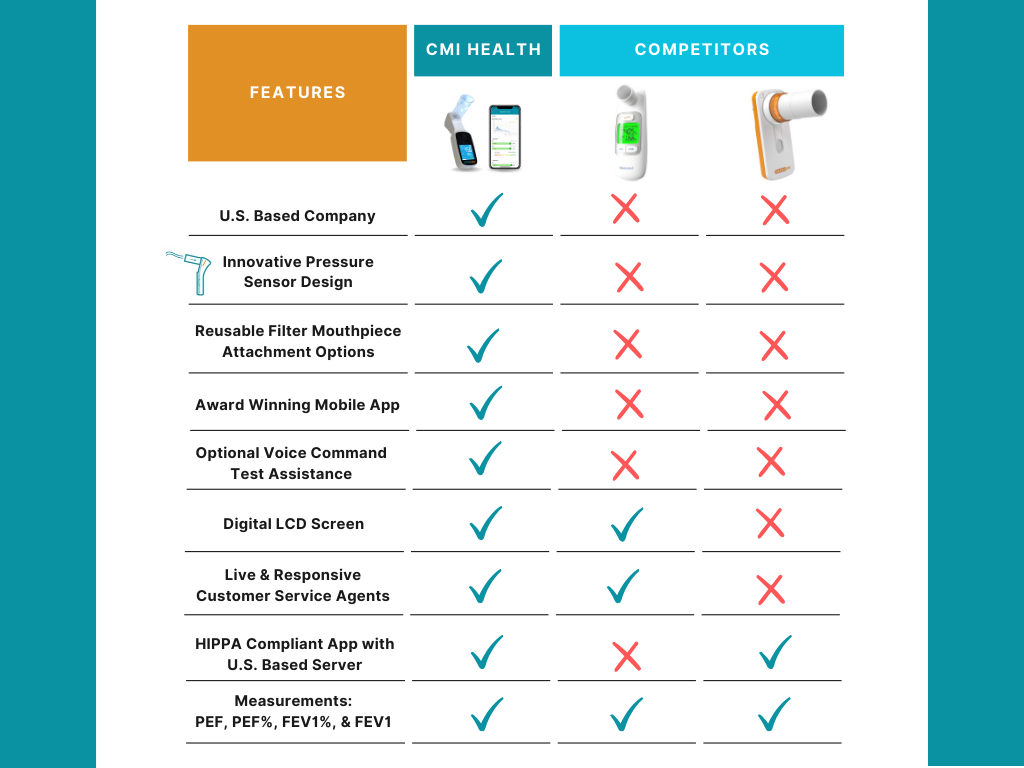
CMI Health provides innovative solutions for remote health monitoring, supporting both personal and professional care.
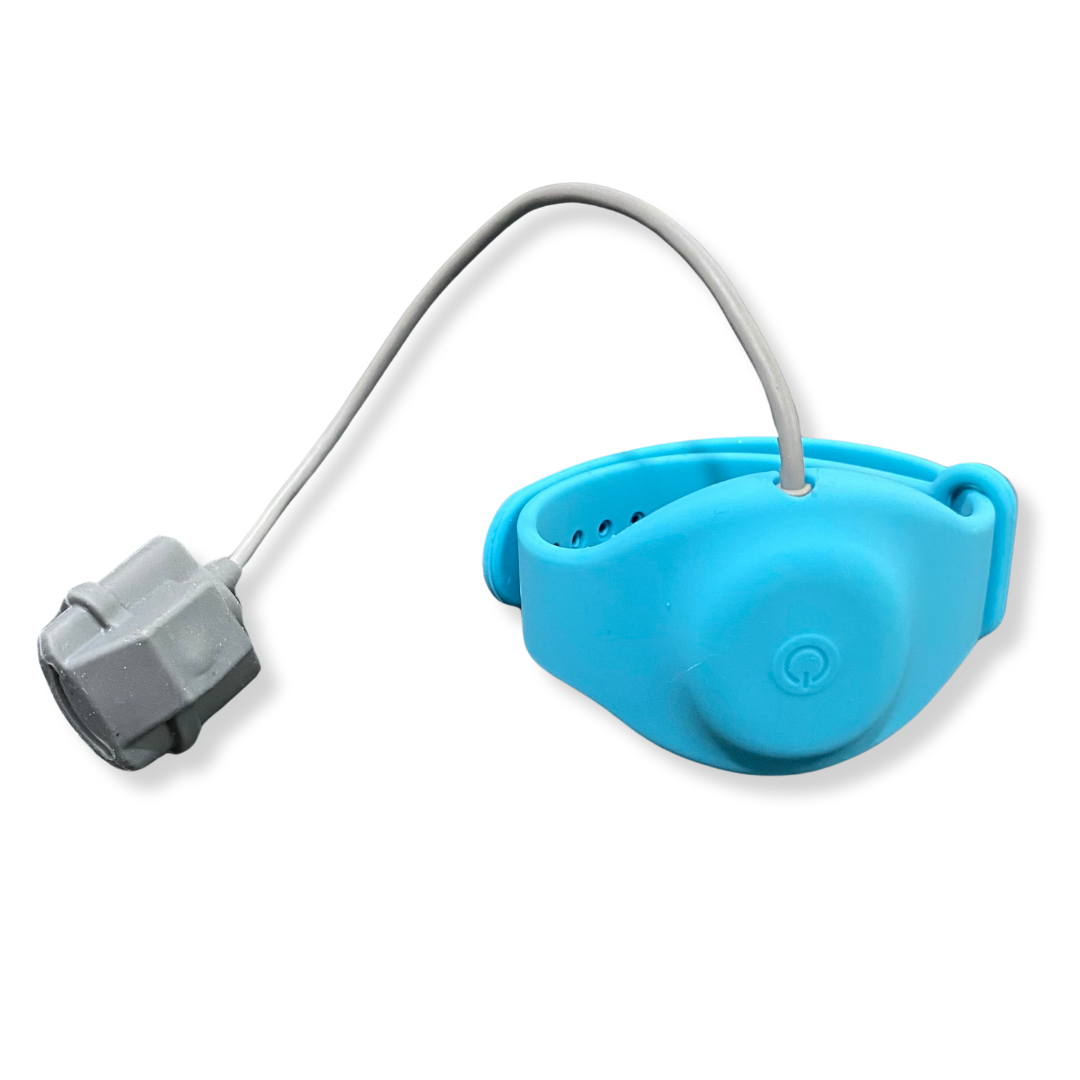
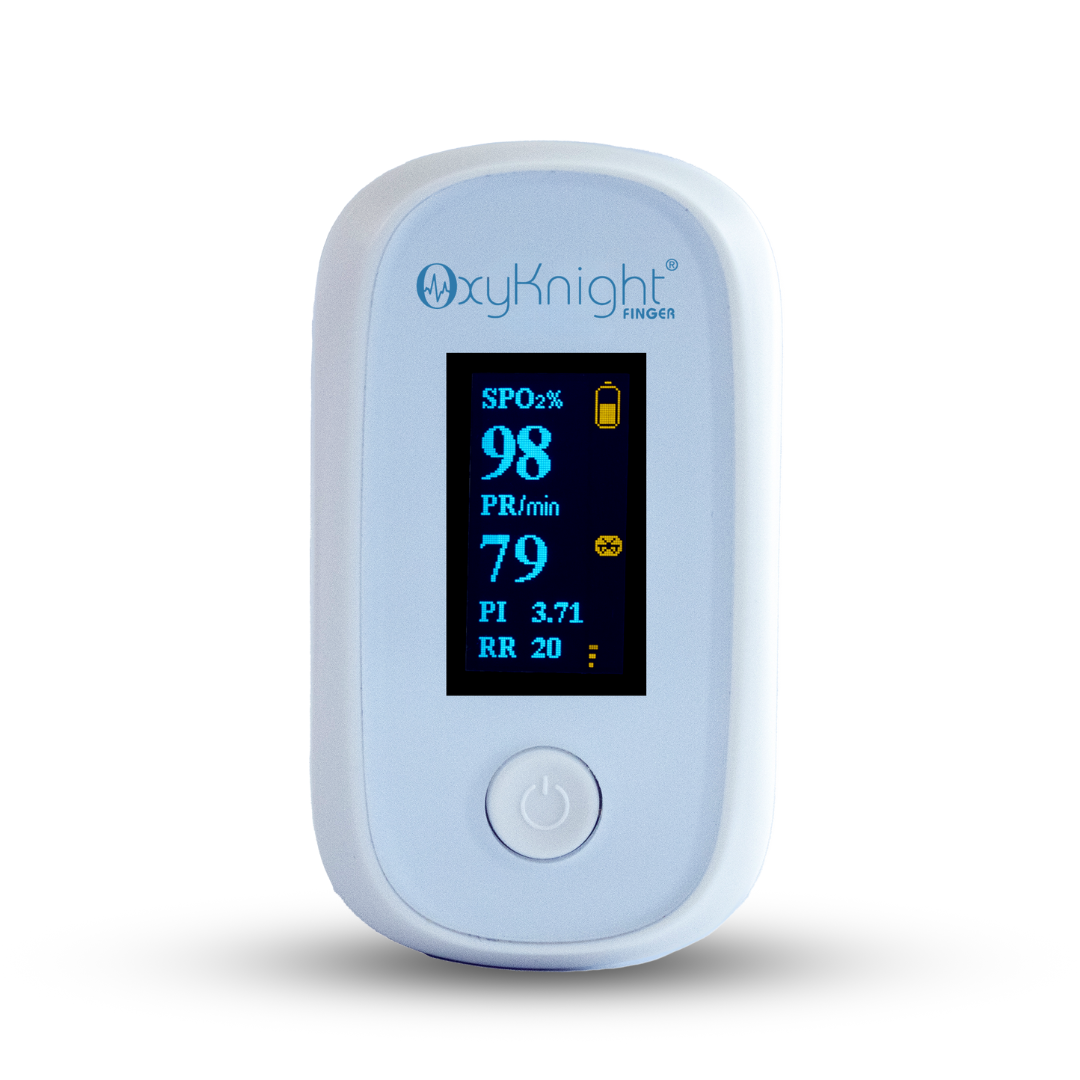
Pulse Oximetry
Digital pulse oximetry devices measure blood oxygen levels and pulse rate in real-time, offering vital health data.
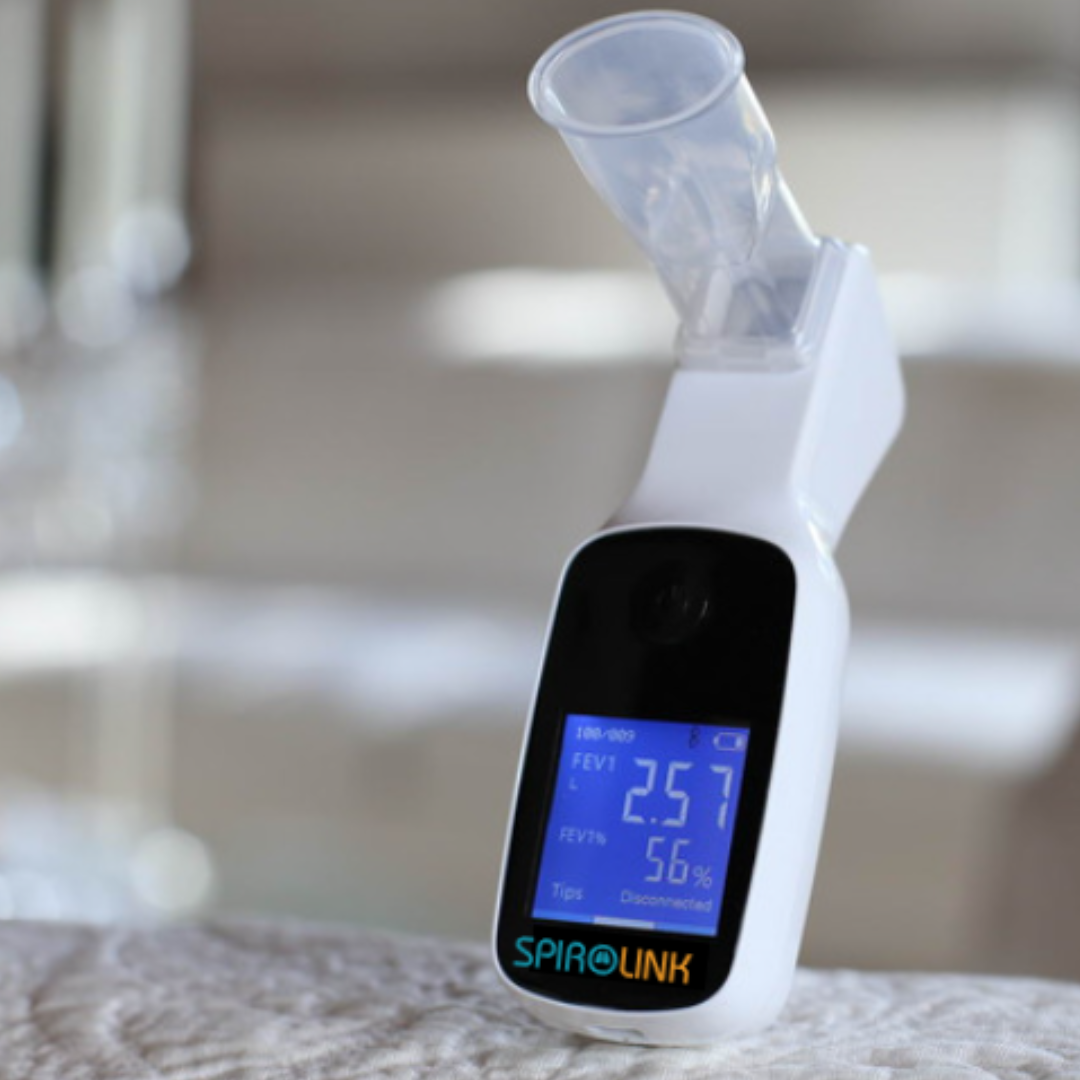
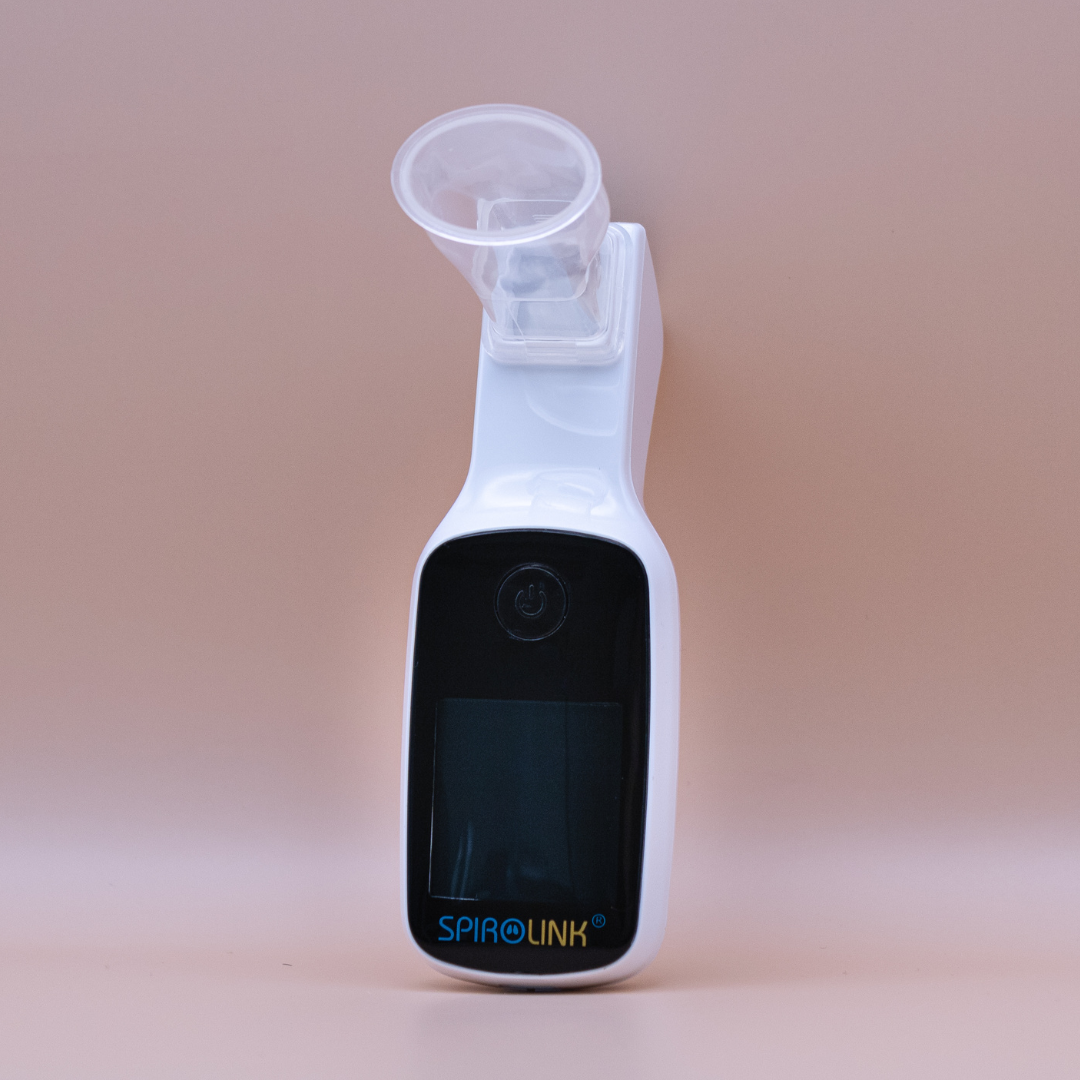
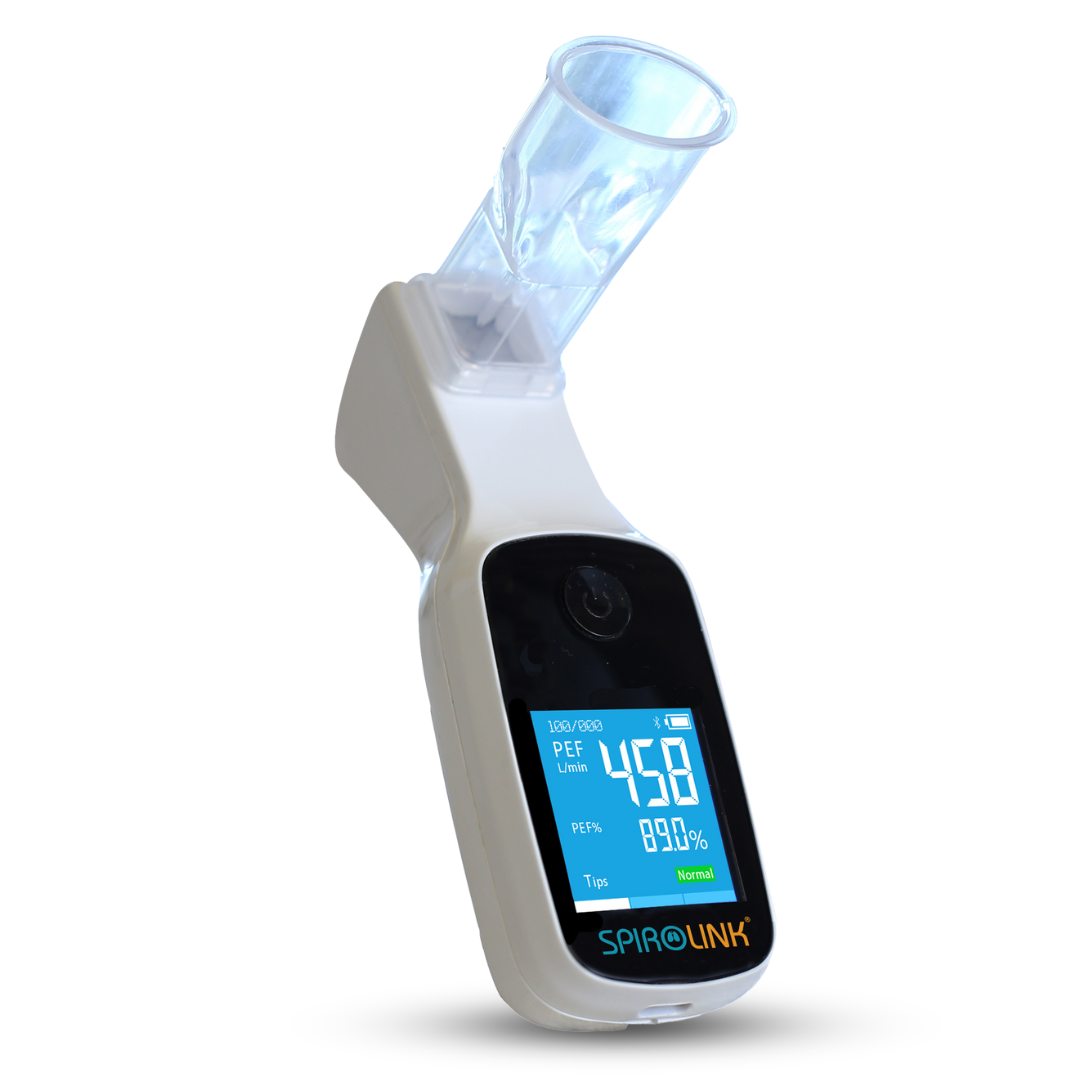
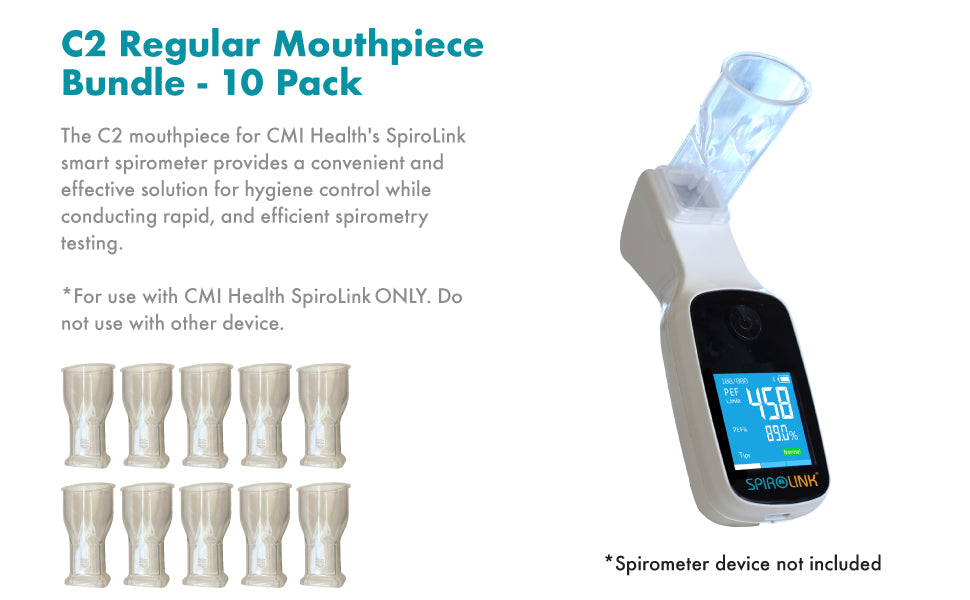
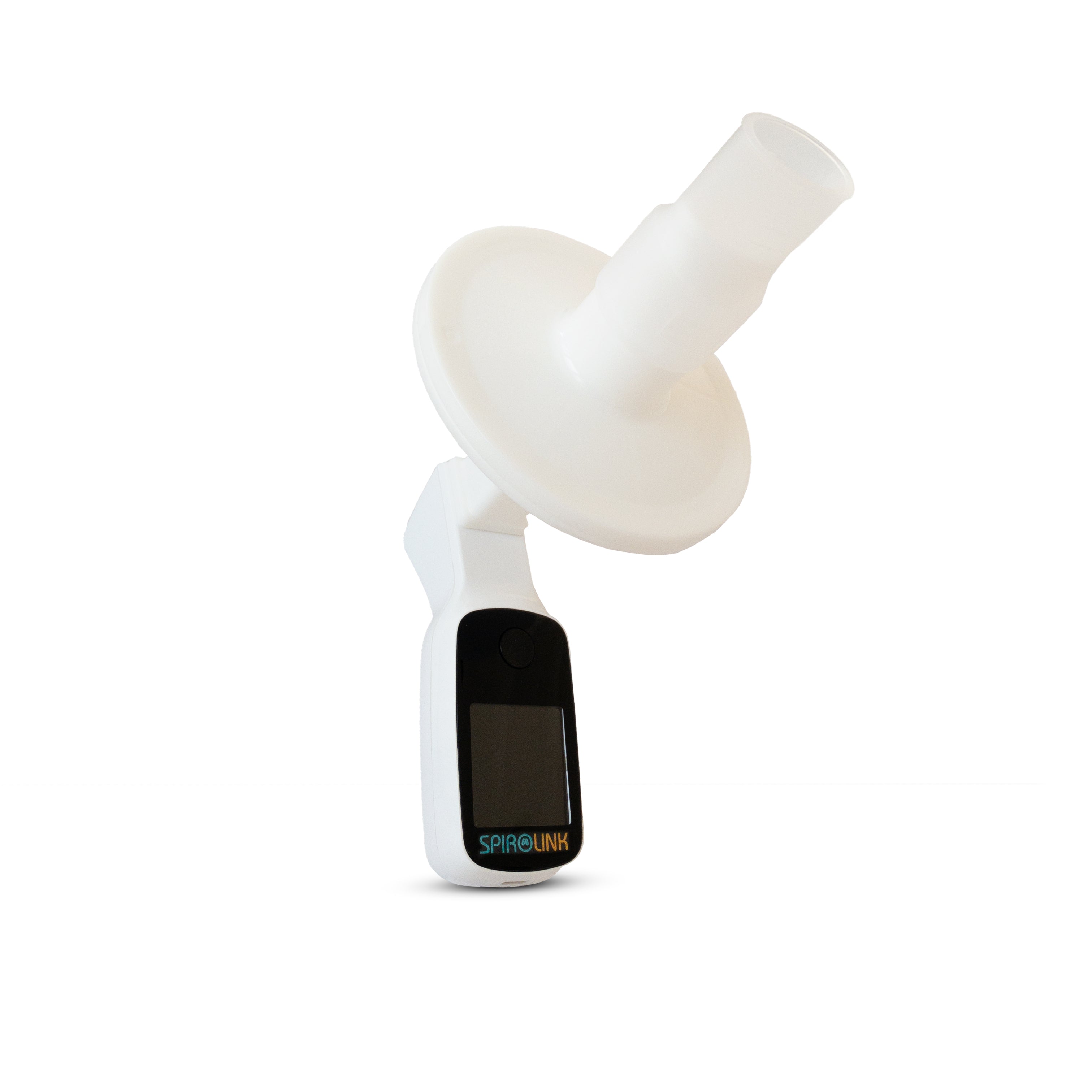
Spirometry
Smart spirometers measure pulmonary function, providing essential data on lung health and enabling effective management.
Vital Sign Monitoring
Professional vital sign monitors track key metrics like oxygen levels , blood pressure, and more with clinical accuracy.