The Importance of Capnography in Emergency and Critical Care

A practical overview of capnography for clinicians—from how it works to where it fits into critical care, sedation, and EMS workflows.
Capnography is a vital diagnostic and monitoring tool for clinicians in emergency medicine, anesthesia, and critical care. By measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO₂) in exhaled breath—specifically the end-tidal CO₂ (EtCO₂)—capnography provides real-time feedback on a patient’s ventilation, circulation, and metabolic function (NIH, 2016).
For emergency medical services (EMS) providers and hospital-based clinicians alike, capnography guides first responders in treatment decisions and proactive care, improving patient stabilization and outcomes. (Respiratory Therapy, 2021).
What Is Capnography?
Capnography is the continuous monitoring of exhaled CO₂ throughout the respiratory cycle. The key measurement—End-Tidal CO2 (EtCO₂)—reflects the maximum amount of CO₂ released at the end of an exhalation.
Because it updates with each breath, capnography offers earlier warning signs of respiratory distress, airway obstruction, or perfusion issues than other common vitals like pulse oximetry or blood pressure.
Capnography provides:
-
EtCO₂ values in mmHg or kPa
-
Real-time respiratory rate
-
A capnogram waveform that visualizes the full breath cycle
What Is a Capnograph and How Does It Work?
A capnograph is the device used to perform capnography. It typically includes:
-
A sampling line that collects exhaled breath
-
A CO₂ sensor
-
A digital display showing EtCO₂ values and waveform
There are two primary types:
-
Mainstream capnographs: measure CO₂ directly at the airway using a sensor placed between the patient and the breathing circuit.
-
Sidestream capnographs: draw a sample of exhaled gas through a small tube to a sensor located inside the monitor.
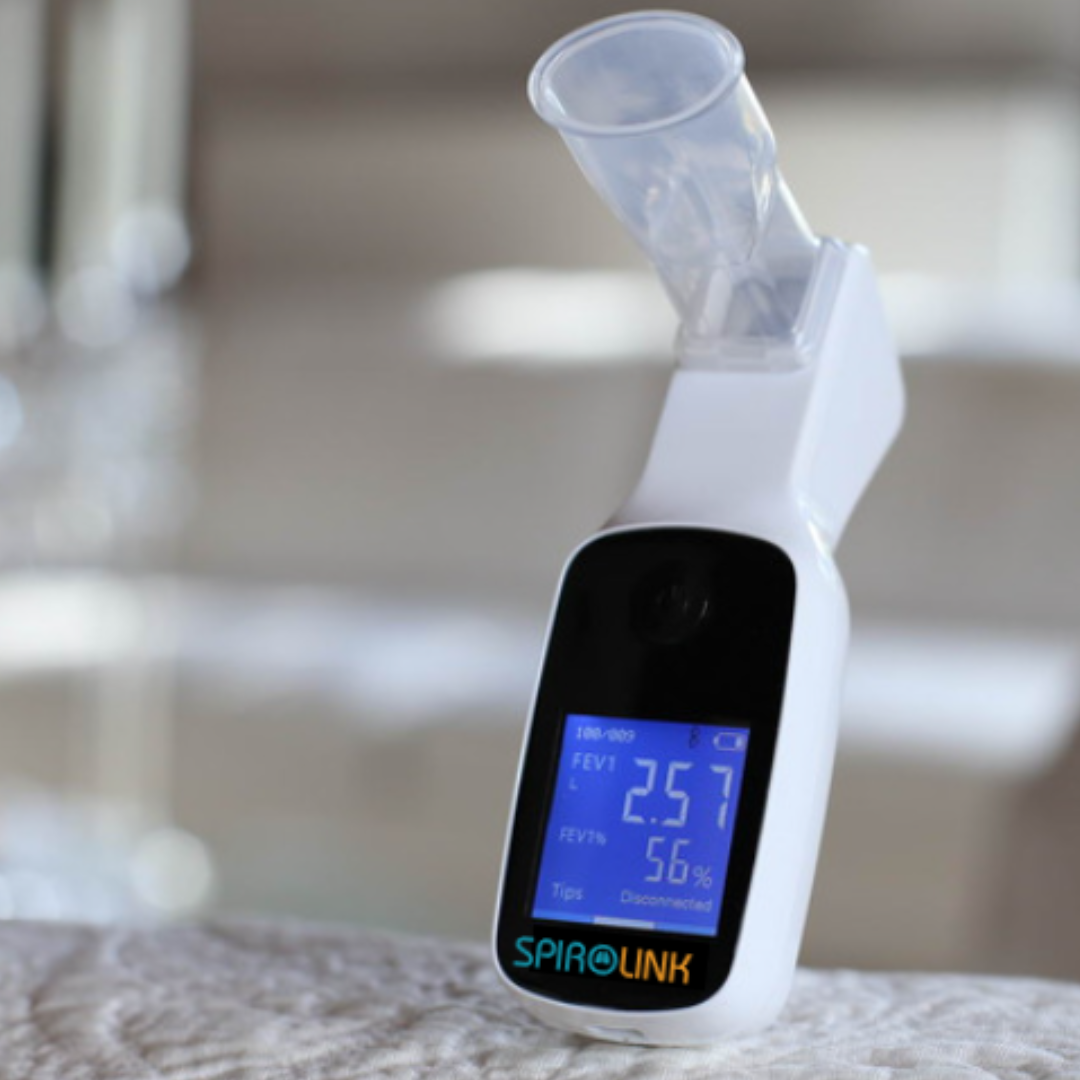
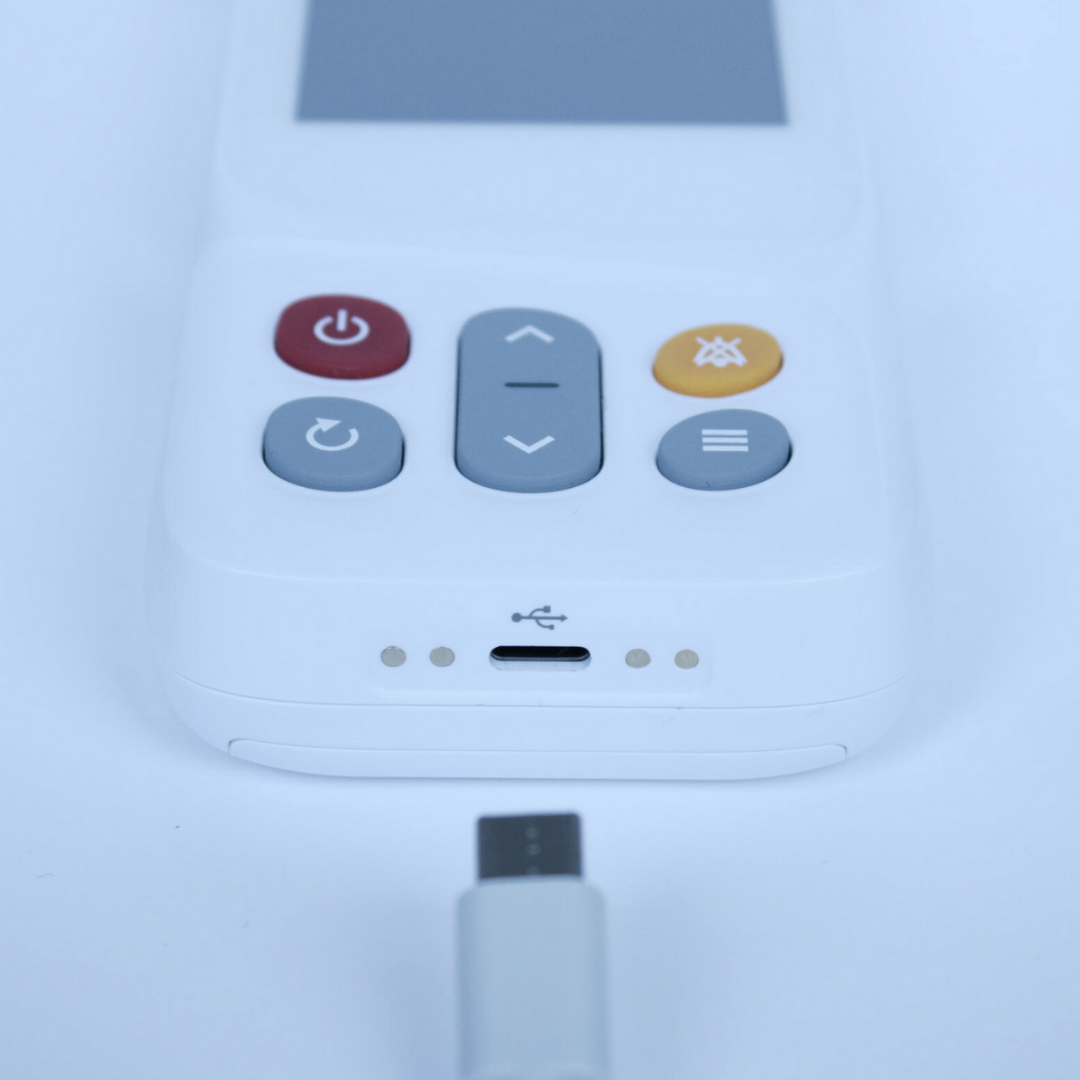
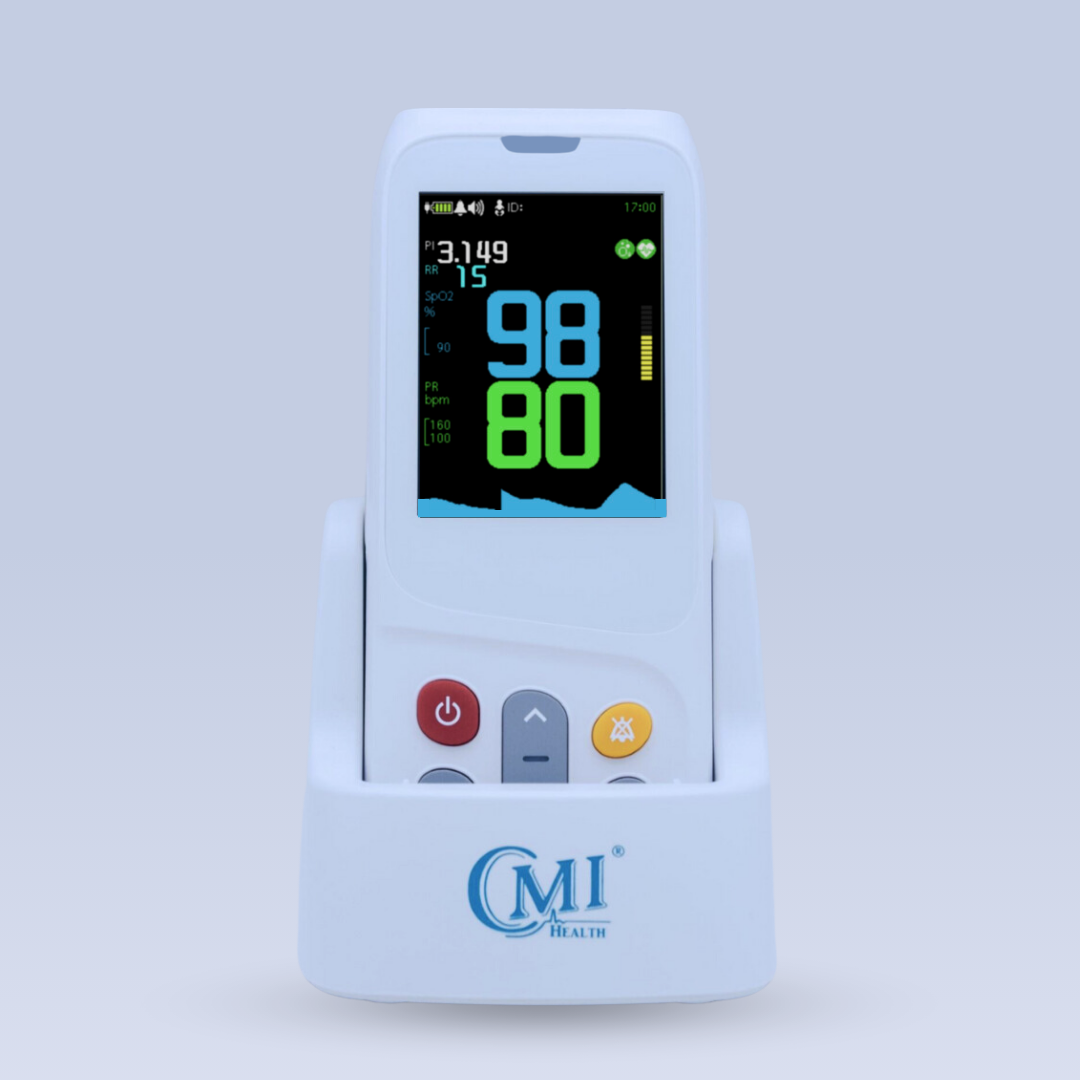
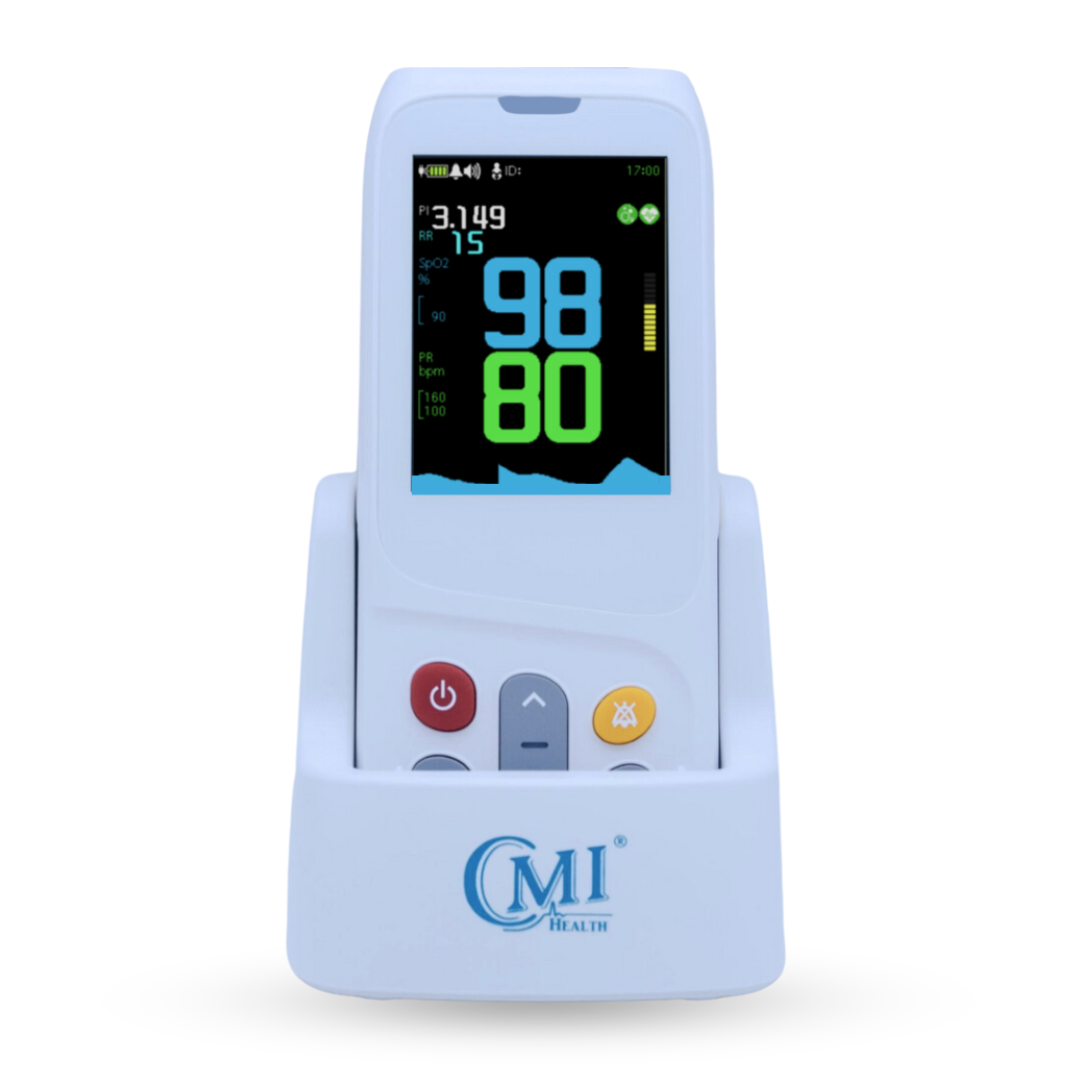
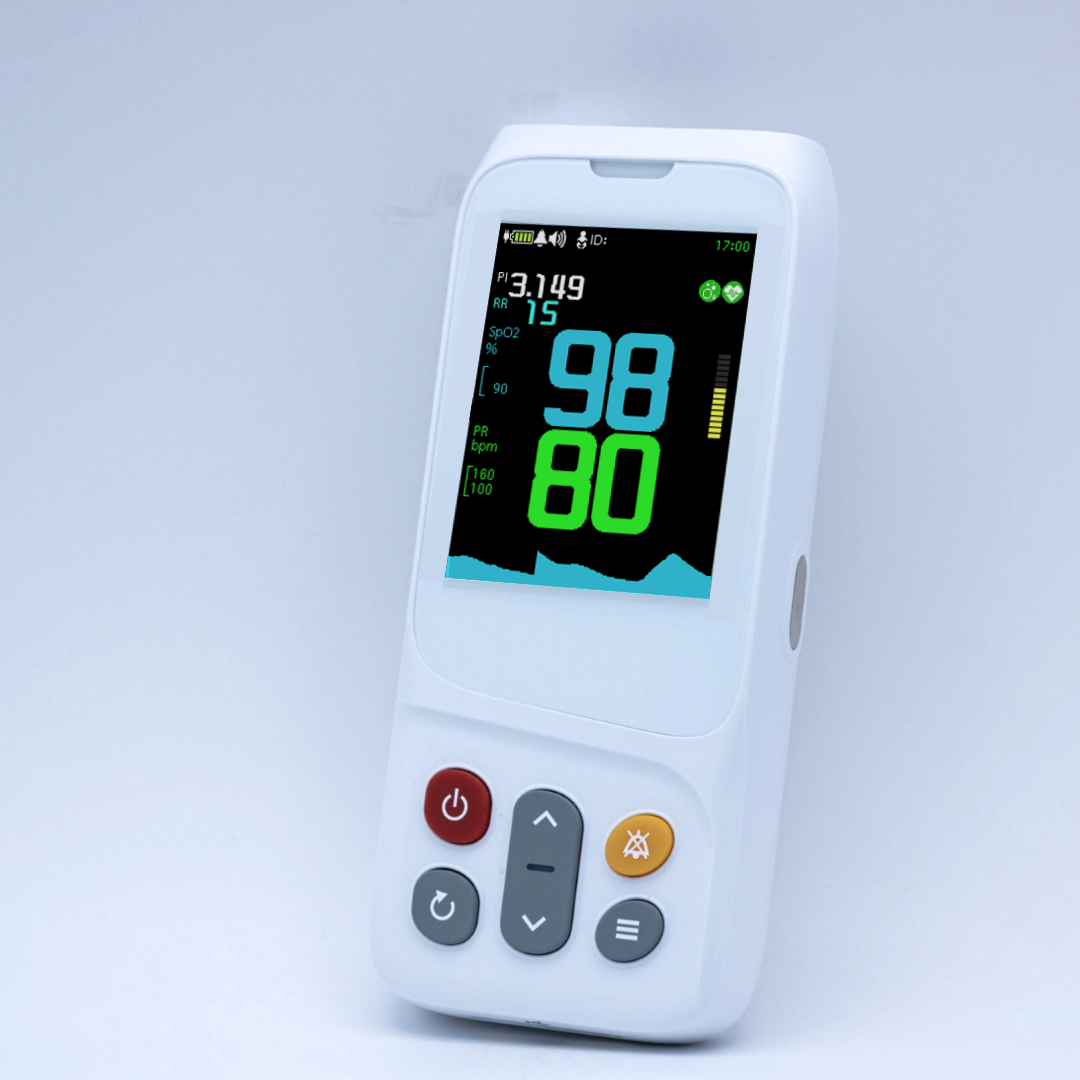
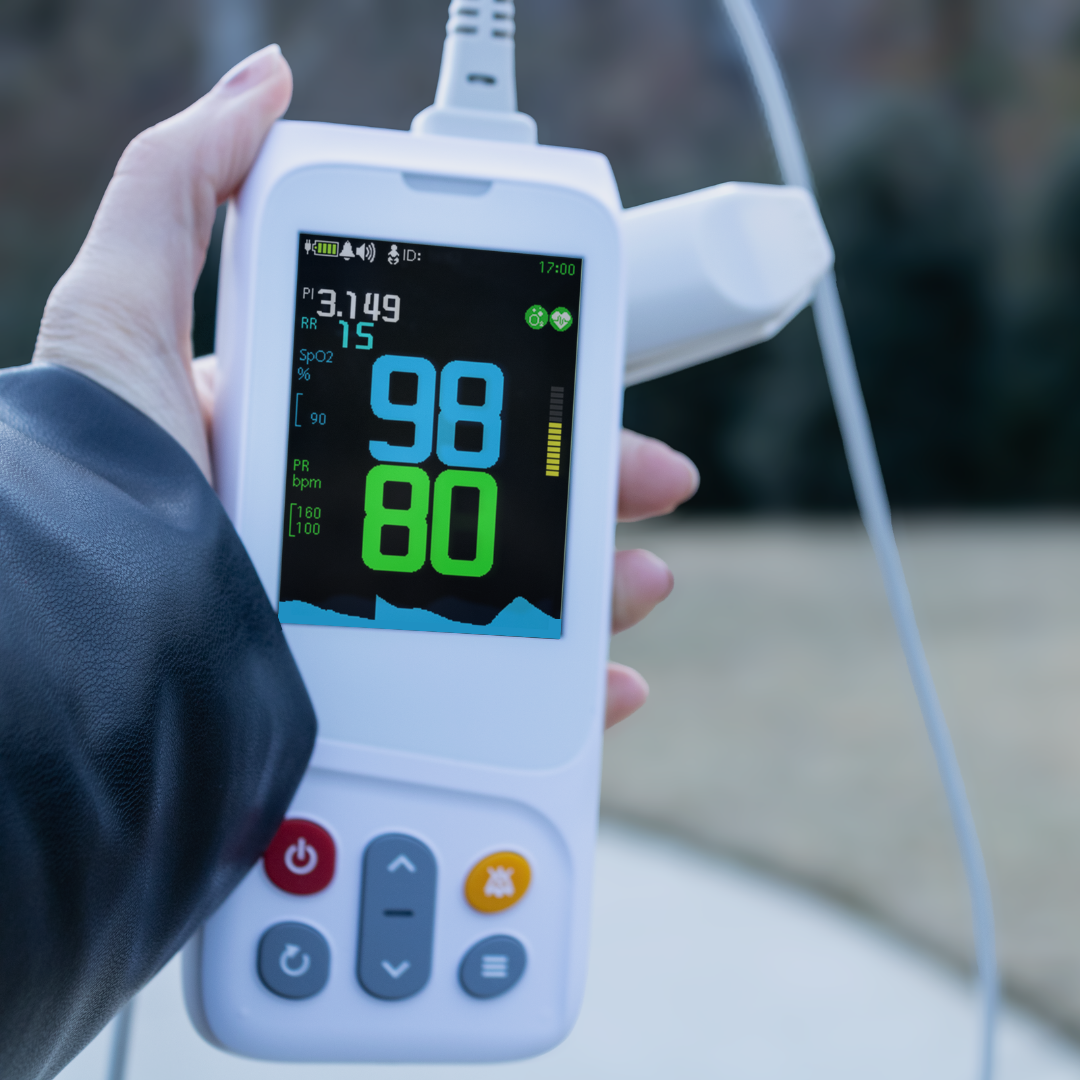
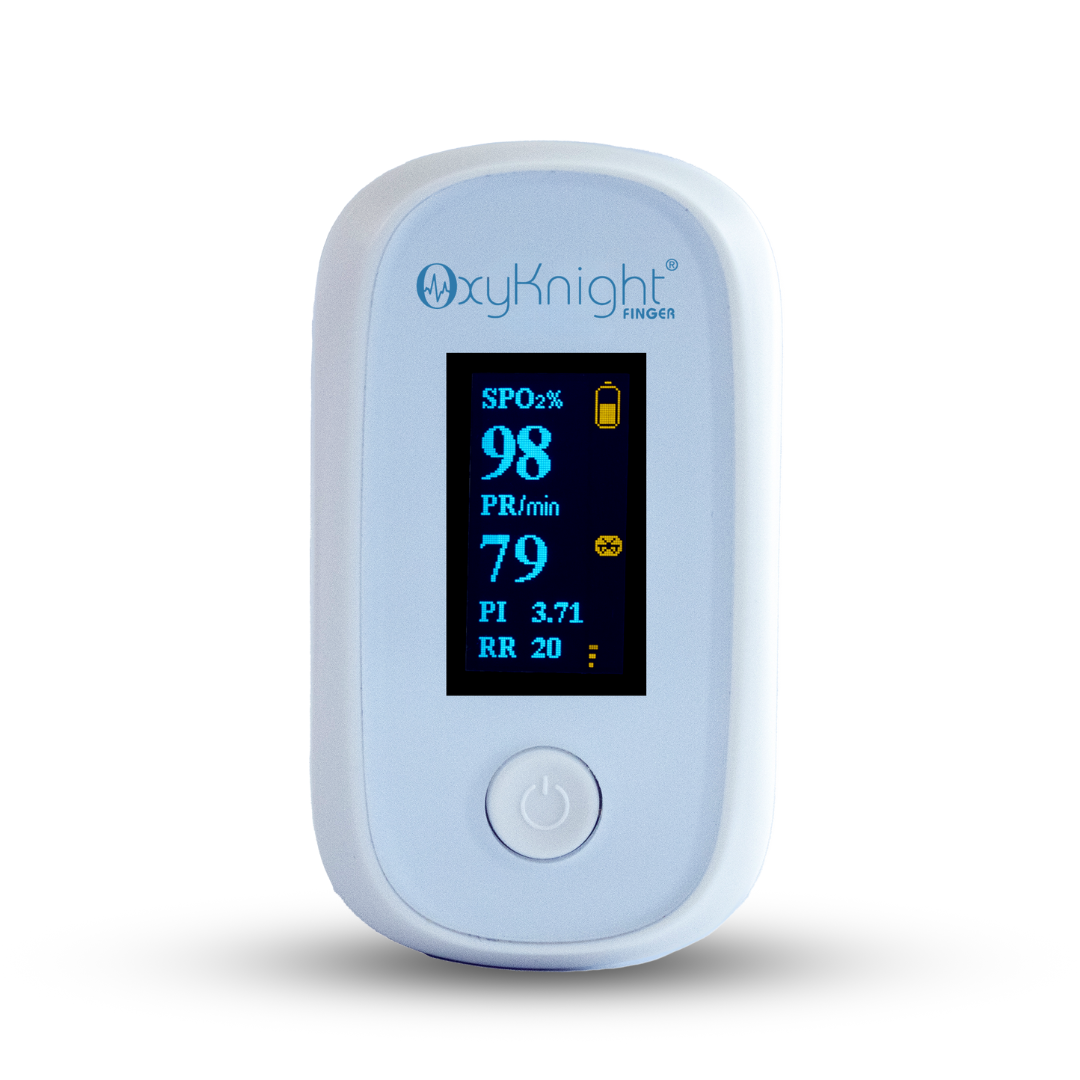
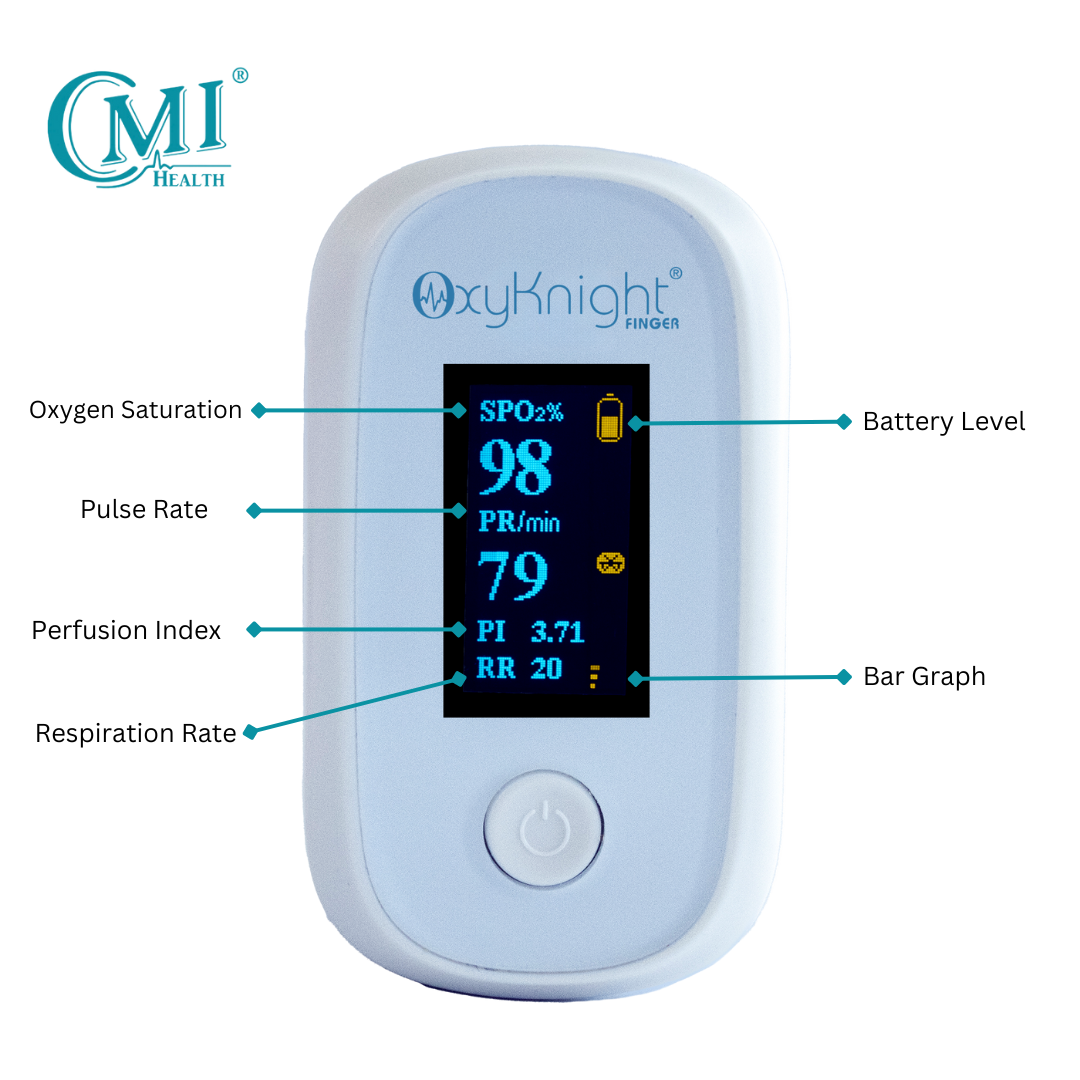
Figure 1-CMI Health's Handheld Capnograph (PC-900B) uses sidestream technology.
Sidestream technology is especially well-suited for portable applications. It’s lightweight, flexible, and compatible with both intubated and non-intubated patients—ideal for EMS and mobile care settings.
How do First Responders Use Capnography?
Capnography provides real-time insights that are critical across a wide range of emergency and acute care scenarios. It supports early detection, confirms treatment effectiveness, and helps prevent complications in time-sensitive environments (NIH, 2016):
-
Airway Integrity & Tube Placement
EtCO₂ is the most reliable method for confirming proper endotracheal tube (ETT) placement. A consistent waveform and CO₂ presence confirm tracheal, not esophageal, intubation. -
Cardiac Arrest & CPR Monitoring
Capnography helps assess the quality of chest compressions during resuscitation. (American Nurse Association, 2012). A rise in EtCO₂ often signals return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), providing a non-invasive indicator without interrupting CPR. -
Procedural Sedation Monitoring
During moderate sedation, capnography detects hypoventilation and apnea earlier than pulse oximetry, allowing for faster intervention. -
Shock, Trauma, and Low Perfusion
Decreased EtCO₂ levels can indicate poor perfusion or the early onset of shock—valuable information in trauma response and critical care transport. Capnography aids in detecting these changes before they manifest in other vital signs (NAEMSP, 2022). -
ICU and Ventilator Monitoring
In intensive care settings, capnography continuously tracks ventilated patients, offering early warning of changes in respiratory status, circuit disconnections, or airway obstructions. -
Intraoperative Monitoring & Complications
EtCO₂ monitoring during surgery can detect air embolism, thromboembolism, and other complications by signaling abnormal respiratory patterns. -
Prehospital and EMS Response
EMS teams rely on capnography for airway management, overdose response, and patient monitoring during transport or resuscitation. EMTs and BLS providers use continuous EtCO₂ monitoring to guide ventilation and assess respiratory distress, cardiac arrest, and trauma cases (NAEMSP, 2017).
In fire or police departments—often first on scene—capnography supports early critical care before ambulances arrive. It helps assess smoke inhalation injuries, determine ventilation needs, and monitor naloxone effectiveness during opioid overdose (NLM, 2020).
Why Portability Matters in Emergency Care
In unpredictable or resource-limited environments, portable capnography gives clinicians immediate insight to act quickly and effectively.
-
Assess respiratory status early, before other vital signs change
-
Verify airway placement quickly and non-invasively
-
Guide CPR by monitoring EtCO₂ trends and detecting ROSC
-
Track patients during transport, identifying deterioration in real time
-
Support toxic exposure response, such as smoke inhalation or opioid overdose
Handheld capnographs bring hospital-grade monitoring to field and prehospital settings—empowering clinicians wherever care happens.
Portable Capnography That Keeps Up with Critical Care
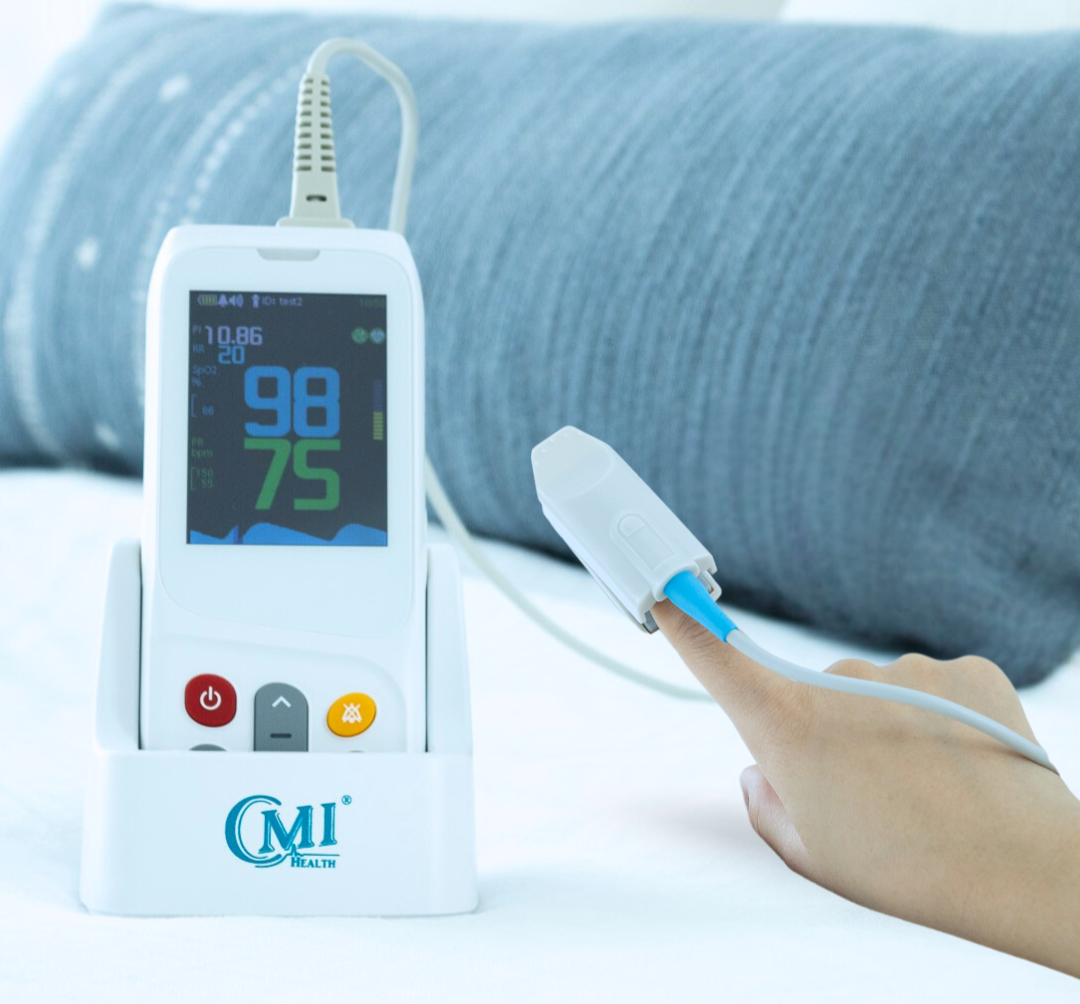
Designed with EMS and frontline clinicians in mind, the CMI Health PC‑900B handheld capnograph provides accurate, real-time respiratory data in the field or at the bedside. It provides continuous EtCO₂ waveform and numerical feedback, alongside key vitals like blood oxygen saturation (SpO₂), respiratory rate, and pulse—making it a compact, all-in-one solution for high-pressure environments.
The PC‑900B is purpose-built for mobility—lightweight, battery-powered, and easy to deploy in emergency kits or transport scenarios. Unlike stationary hospital units that require fixed setups and continuous power, it functions reliably in the field, from triage zones to remote rescues.
It’s also a cost-effective option for EMS teams, offering customizable accessories to meet diverse patient needs. With a blend of portability, accuracy, and affordability, the PC‑900B helps providers deliver fast, informed care when it matters most.
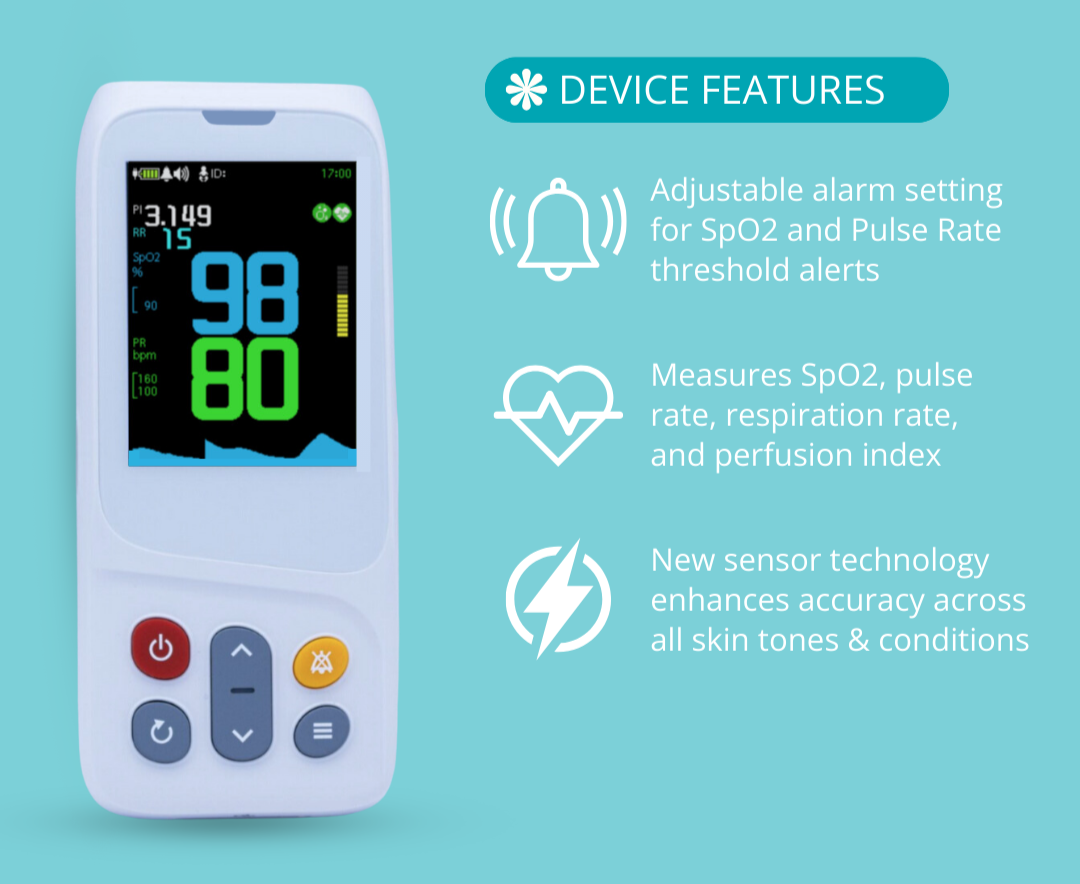
PC‑900B | Handheld Capnograph Key Features
-
Real-Time EtCO₂ Monitoring: Provides instant numerical and waveform feedback on airway status, CPR effectiveness, and respiratory distress.
-
Continuous Monitoring During CPR: Tracks EtCO₂ levels throughout chest compressions and helps detect return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
-
Essential for CPR and Intubation: Verifies airway placement and supports ventilation success in both intubated and non-intubated patients.
-
Portable and Compact: Lightweight and battery-powered for easy deployment in field scenarios, emergency kits, or transport settings.
-
Elegant Interface: User-friendly design supports fast interpretation and efficient care in dynamic clinical environments.
-
Affordable: Offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional hospital-based capnography units.
-
Multi-Functional for Emergency Use: Measures EtCO₂, SpO₂, respiration rate, and pulse—delivering complete patient data in a single device.
-
Immediate Respiratory Assessment: System response time is under one second, ensuring fast, actionable feedback in critical moments.
→ Learn more and equip your team today: https://www.cmihealth.com/collections/capnography
→ See how our best-selling medical devices can help you today https://www.cmihealth.com/pages/products
Have any questions about our products or just want to chat? Feel free to email us at info@cmihealth.com or call at 888-985-1125 (ext. 1).























Leave a comment