4 Ways You Can Improve Your Blood Oxygen Saturation | CMI Health

This blog post was originally released in January 2021 and has been updated as of February 2022 with additional information.
Blood oxygen saturation is a measurement of how much oxygen you have flowing through your veins at a given time. As such, it’s the key to determining whether your body is getting enough of this element to survive. In the average individual, blood oxygen saturation often reads between 95 and 100 percent (Shaikh, 2020).
As such, it’s the key to determining whether your body is getting enough of this element to survive.
However, for those suffering from a condition that makes it difficult to breathe, this range may be much lower, resulting in a series of additional health problems.
For example, if you experience symptoms such as:
· Shortness of breath
· Chest pains
· Elevated heart rate
· Dizziness
· Headaches
· Blurry vision
· High blood pressure
Then chances are, your blood oxygen levels are low. These are a few ways to improve your blood oxygen saturation and control your symptoms
Get Plenty of Fresh Air
First and foremost, it’s important that you go to the effort of breathing fresher air. This means spending some time outdoors or opening your windows during the warmer months. Unfortunately, there are many things that can affect your home’s indoor air quality, which can make it more difficult for you to breathe, depending on your condition. So, outdoor air is considered the best way to get more oxygen into your lungs and, therefore, increase your blood oxygen saturation.
Maintain an Exercise Routine
You can also make a difference by adopting and sticking to a regular exercise routine. The lungs require a certain amount of training in order to draw in more oxygen and process it at a reasonable pace. Exercise helps with this, as it increases the rate that your body uses oxygen, thereby prompting your lungs to breathe deeper. Over time, this can improve your endurance, increase your lung capacity, and help raise the amount of oxygen you have in your blood.
Practice Proper Breathing Techniques
Make sure that you’re practicing proper breathing methods as well. Though we breathe constantly, there are actually more effective ways to do so that often go underutilized. For instance, diaphragmic breathing can improve blood oxygen saturation by allowing you to draw in more air and contain it longer in your lungs (Shinde, 2020). This gives the oxygen time to absorb and helps your body get the most out of each breath.
Drink Lots of Water
Drinking lots of water ensures that your lungs stay adequately hydrated, which in turn improves their ability to oxygenate and expel carbon dioxide. Therefore, the oxygen saturation level of your body improves. On average, we lose about 400 milliliters of water per day. So drinking 2-3 liters of water may improve your blood's oxygen saturation level by up to 5 percent. In addition, drinking lots of water regulates body temperature and boosts immunity.
Have Good Posture
One study found that the average oxygen saturation value when measured while sitting in an upright position in a chair was significantly higher than that calculated when the individual was lying on the right or left side of the body (National Library of Medicine, 2016).
Incorrect posture such as slouching can cause the lungs to compress, resulting in difficult breathing and reduced respiratory function. Practicing good posture is essential because this will increase your lung capacity, making breathing easier. With your breathing improved, healthy exercises such as walking, running, and swimming becomes easier over time.
Don’t Smoke
Smoking is the number one cause of lung disease, contributing to COPD and lunch cancer. Smoking causes chronic inflammation in the lungs, making breathing more laborsome and destroying lung tissue. For example, when you exercise, you need oxygen in your muscles. Cigarettes contain carbon monoxide, reducing the amount of oxygen available in your body. Carbon monoxide binds to the hemoglobin in your red blood cells, preventing oxygen.
Get House Plants
Indoor plants can significantly remove organic chemicals from indoor air (NASA, 2013). In addition to essential photosynthesis that releases carbon dioxide and returns oxygen to the air, plants can remove toxicants from the air, soil, and water in at least two ways (PMC, 2011). One study even suggests that active interaction with indoor plants can reduce physiological and psychological stress compared with mental work (PMC, 2015). Some great options include Bamboo Palm, English Ivy, and Areca Palms.
Eat Iron-rich Foods
To increase oxygen in your body, consume foods and drinks that contain iron, nitrates, and vitamins, which is the key to increasing oxygen supply in your body. Good examples are beetroots, leafy vegetables, mushrooms, carrots, kiwi, pomegranate, garlic, nuts, sunflower seeds, meat, fish, eggs, and legumes. One study found that Vitamin D-deficient Korean women had a higher risk of anemia (Science Direct, 2013).
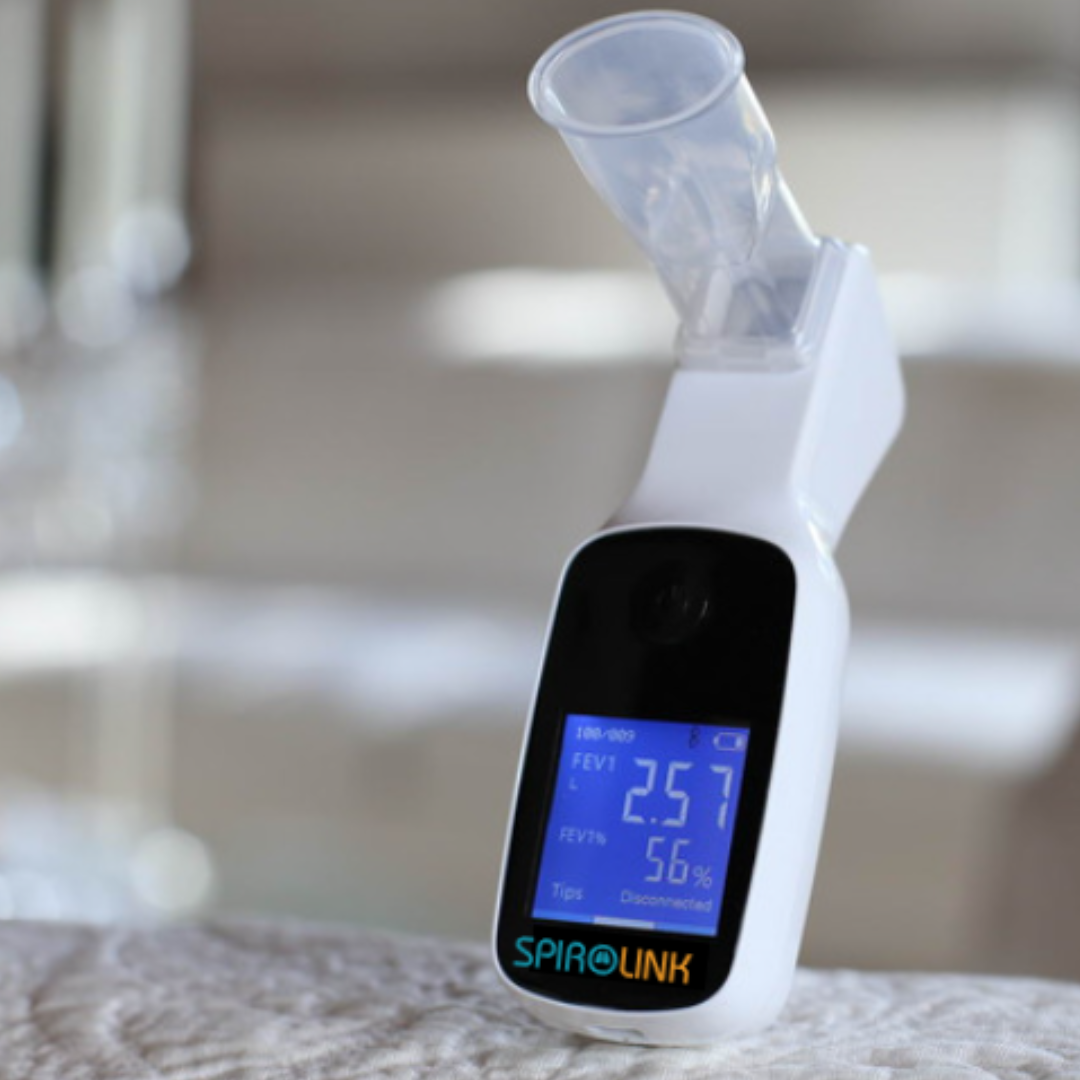
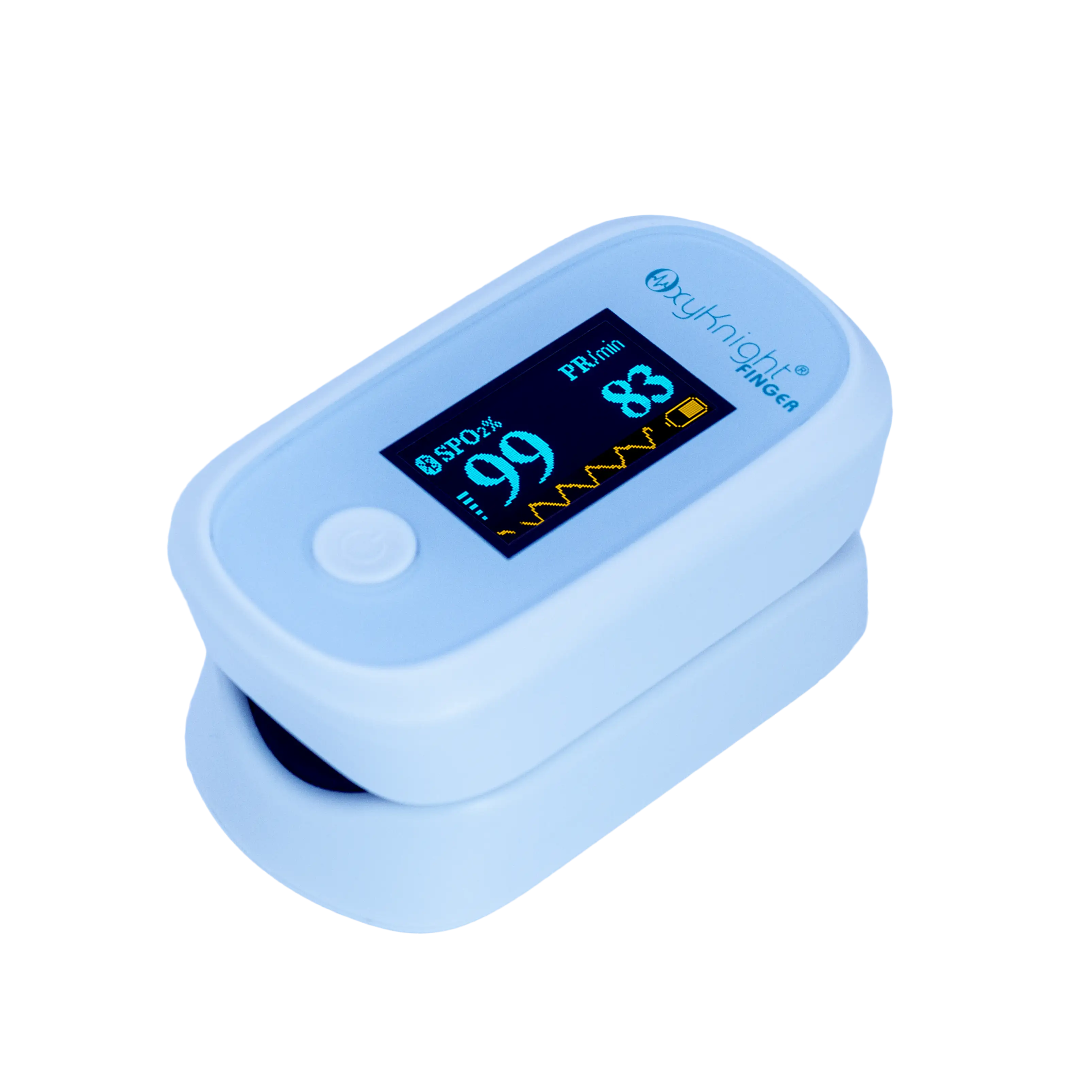
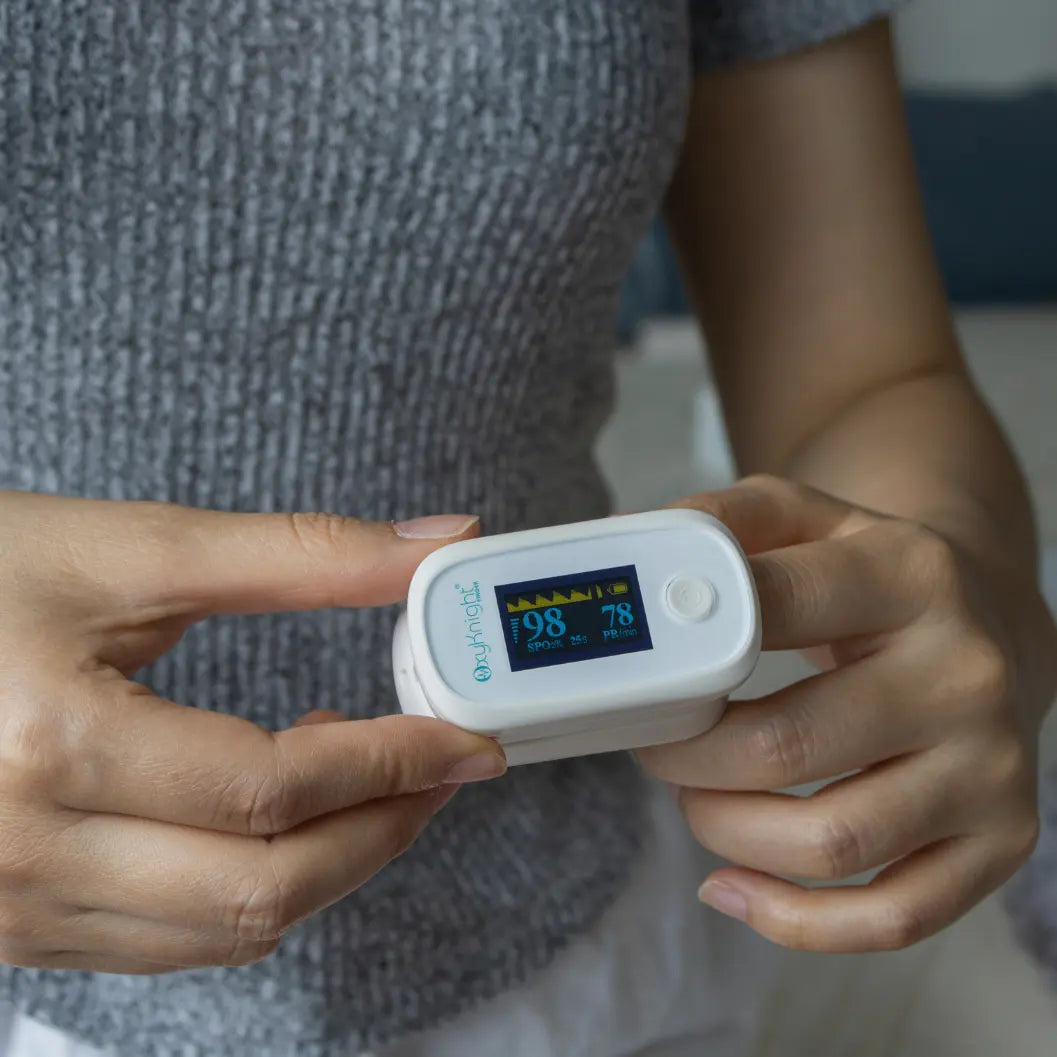
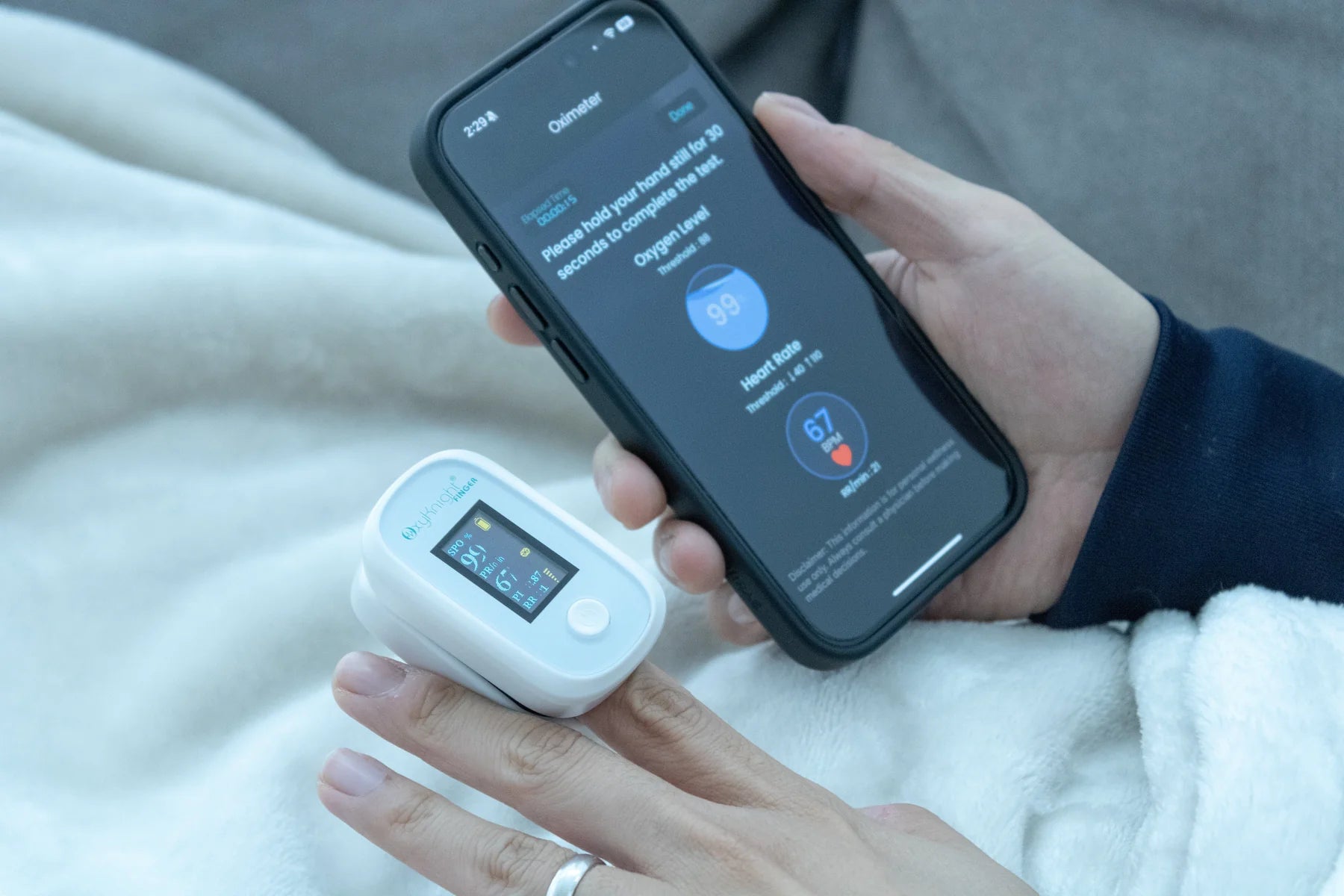
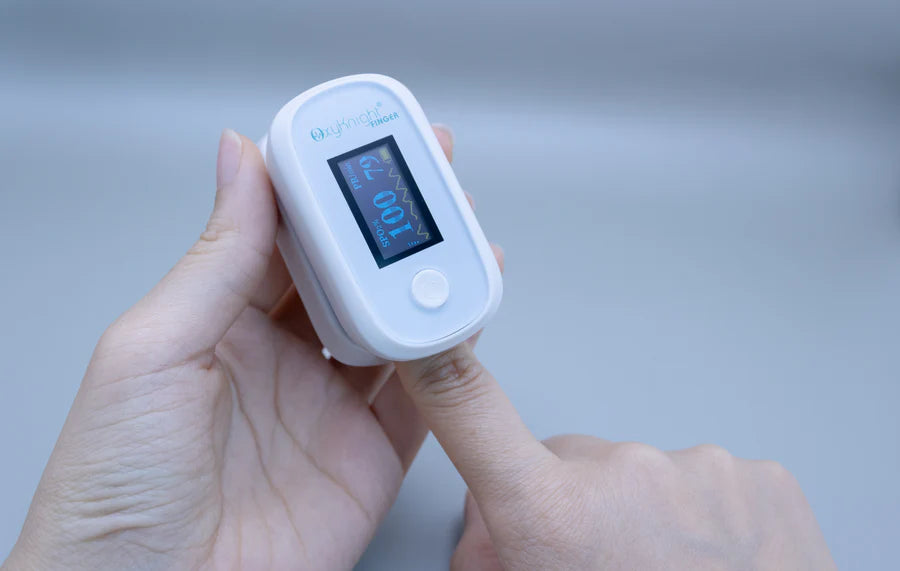
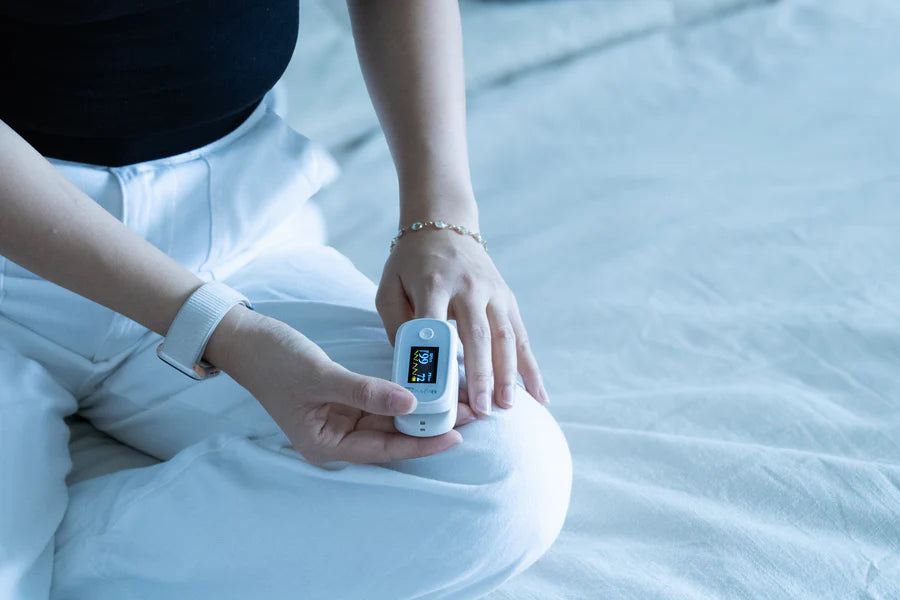
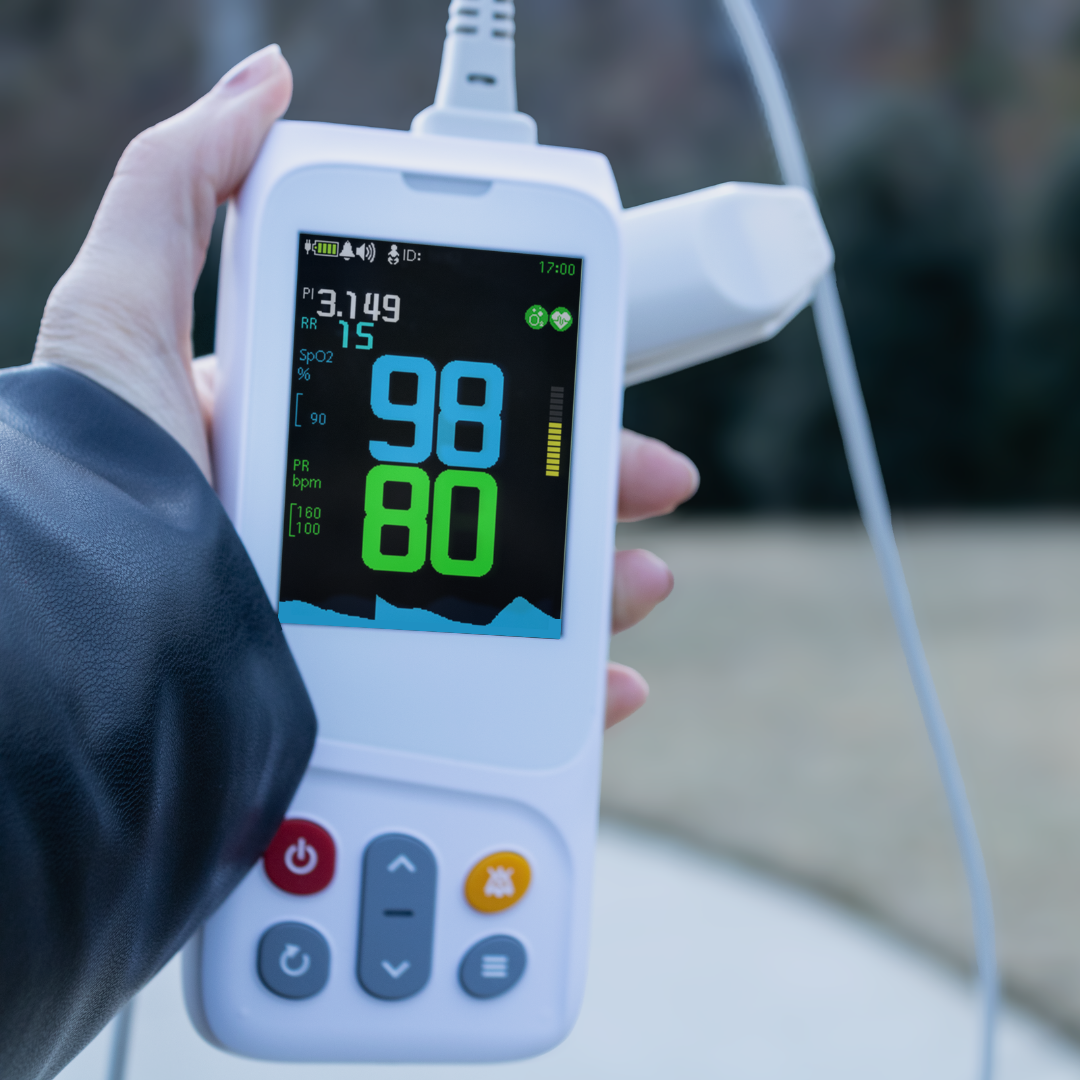
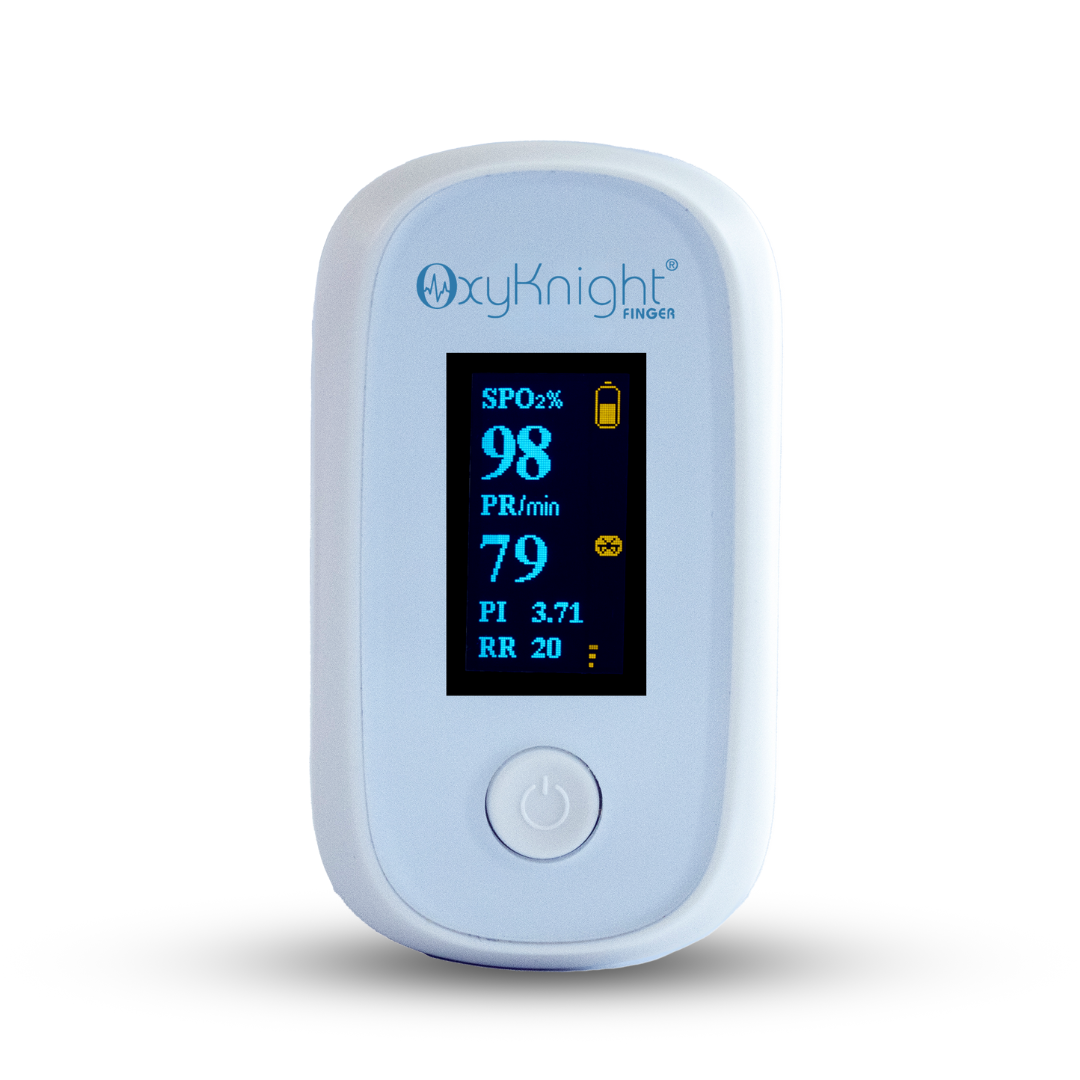
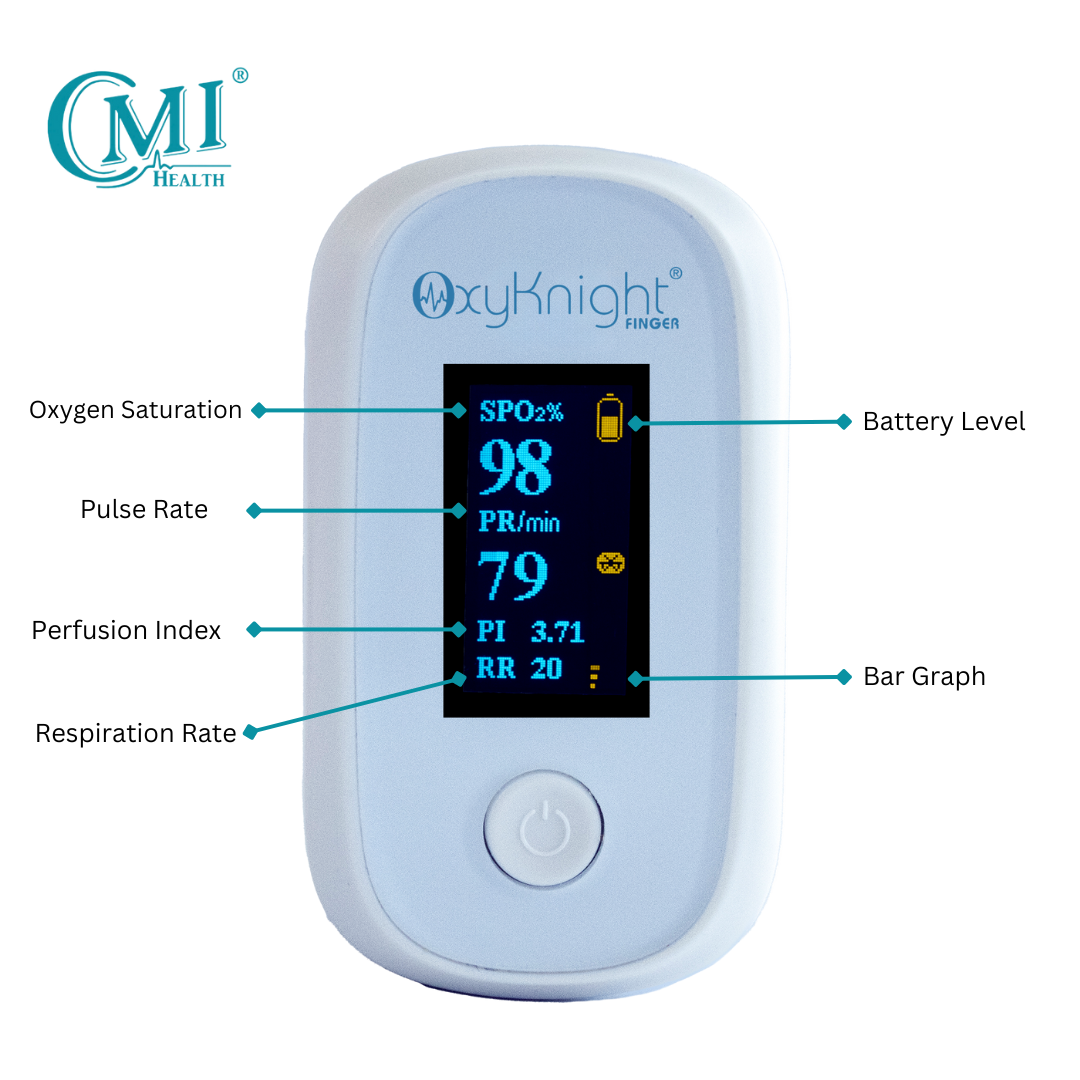
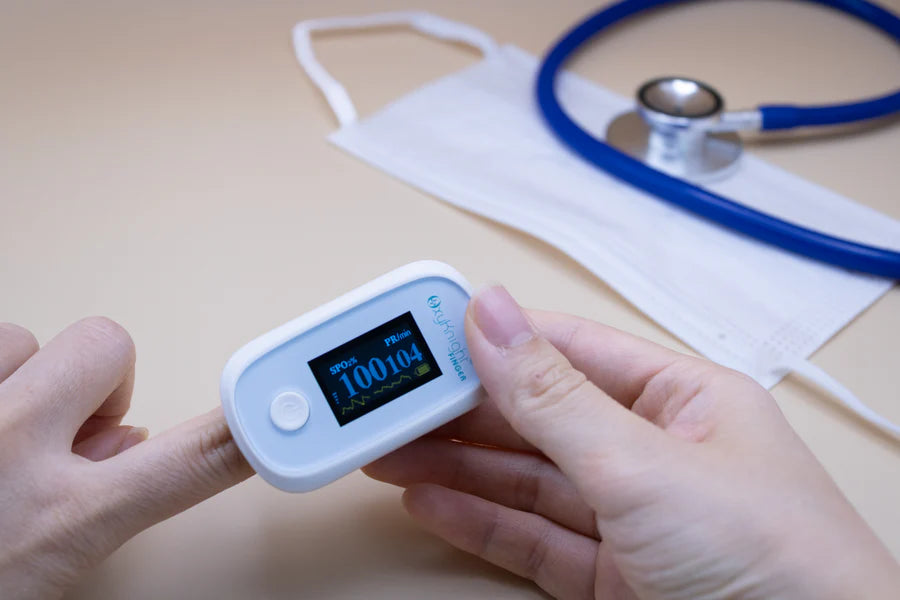
Track Your Levels With a Pulse Oximeter
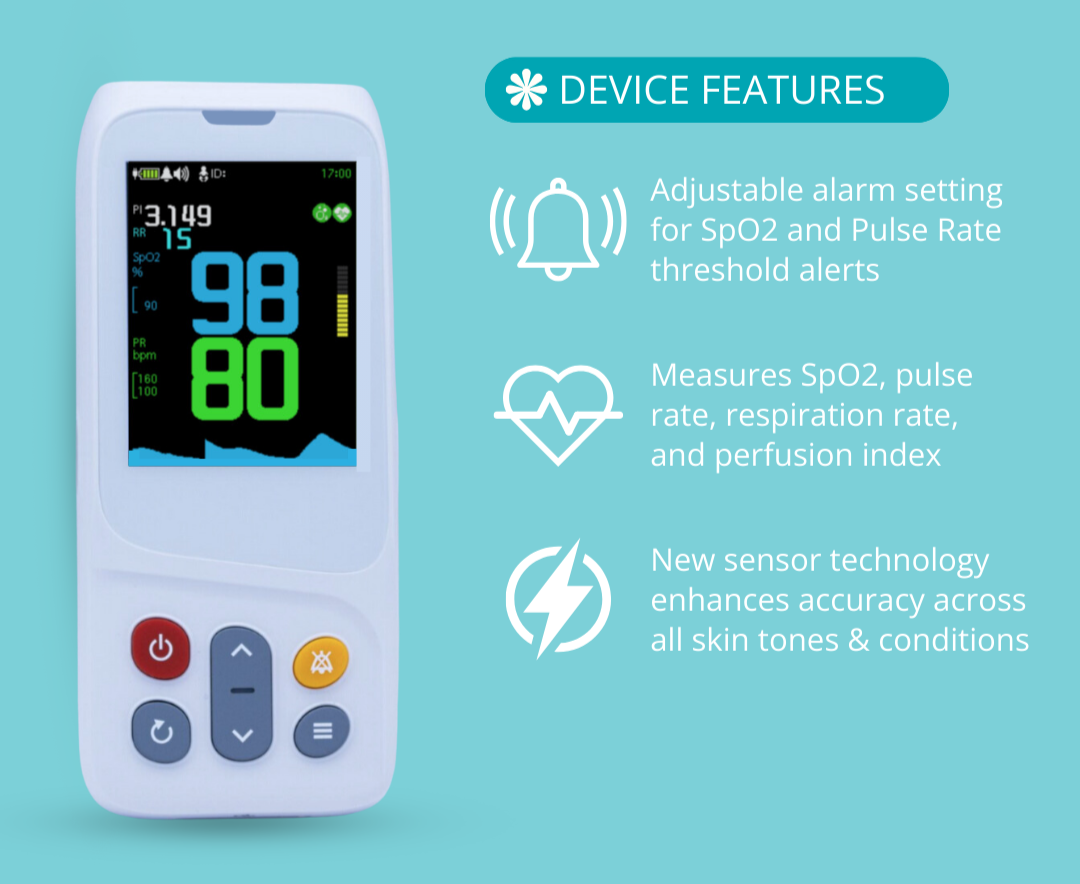
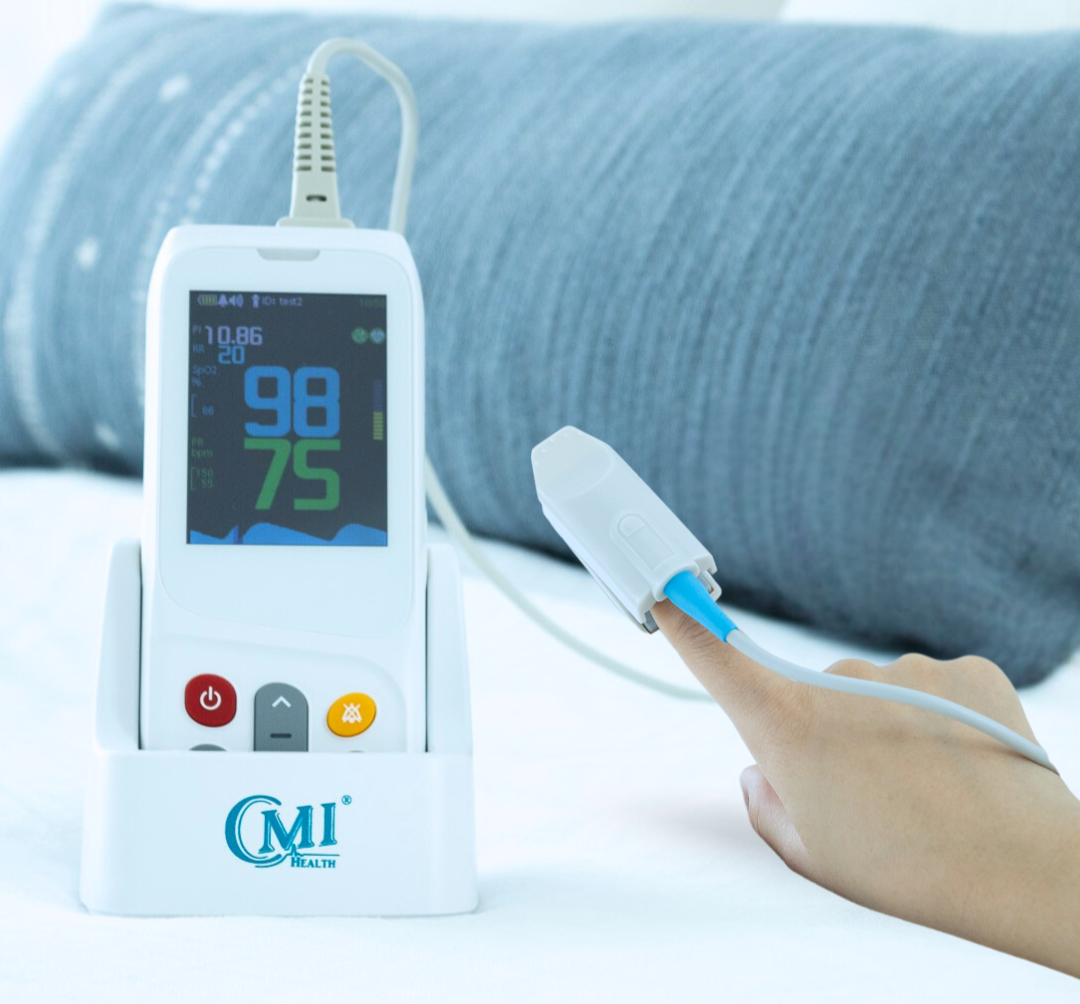
Another effective way you can improve your blood oxygen saturation is by regularly tracking it with a pulse oximeter. Since there’s no way to tell on the surface how much oxygen you currently have, oxygen monitoring is crucial to determining whether your oxygen levels are normal or not and if you may need breathing assistance. Making note of your percentages can also help your doctors determine the best course of treatment.
(See our blog post, Normal Readings on a Pulse Oximeter)
Our handheld oxygen monitoring devices are specifically designed to be easy to use and accurate. This way, we can ensure that tracking and managing your respiratory health is simple, quick, and provides you with all the necessary information you need, to make educated decisions on your health.
Click here to browse the entire collection of CMI Health pulse oximeters and health monitoring devices.























Leave a comment